- A-44, Behind Assotech, Zeta - 01, Greater Noida
services
Solar Inverter and Batteries
Solar Inverter: A solar inverter is an electronic device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes, businesses, and the electrical grid.
Batteries for Solar Energy Storage: Batteries for solar energy storage are rechargeable energy storage systems used to store excess electricity generated by solar panels for later use during periods of low sunlight or high demand.
Here are key features of Solar Inverter:
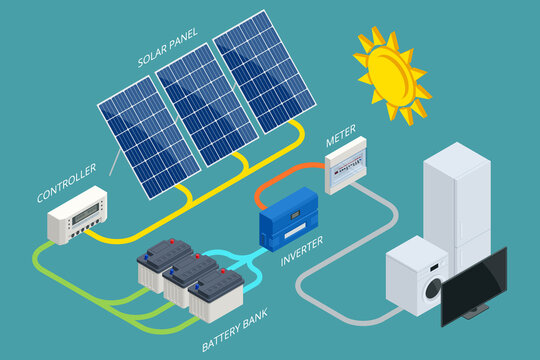
- DC to AC Conversion: Solar inverters perform the crucial function of converting the DC power produced by solar panels into AC power, which is compatible with standard electrical appliances and the grid.
- Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): Many modern solar inverters are equipped with MPPT technology, which optimizes the efficiency of solar power generation by continuously adjusting the voltage and current to extract the maximum power from the solar panels under varying sunlight conditions.
- Grid Connection Grid-tied inverters enable the seamless integration of solar power systems with the utility grid, allowing excess electricity to be exported to the grid for credit or compensation and ensuring uninterrupted power supply when solar energy is insufficient.
- Isolation and Safety: Solar inverters include built-in safety features such as isolation transformers, ground fault protection, and surge suppression to ensure the safety of both the electrical system and personnel.
- Monitoring and Data Logging: Many solar inverters come with monitoring and data logging capabilities, allowing users to track energy production, system performance, and faults remotely via online portals or mobile apps.
- Efficiency and Reliability: High-quality solar inverters offer high efficiency ratings and reliability, minimizing energy losses and ensuring consistent performance over the lifespan of the solar power system.
- Grid Support Functions: Some advanced inverters offer grid support functions such as reactive power control, voltage regulation, and frequency response to enhance grid stability and reliability, especially in systems with high solar penetration.
Here are key features of Solar Inverter:
- Energy Storage Capacity: Solar batteries come in various capacities to store surplus solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy weather, providing backup power and increasing self-consumption of solar energy.
- Chemistry and Technology: Common types of batteries used in solar energy storage systems include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and flow batteries, each offering different characteristics in terms of energy density, cycle life, efficiency, and cost.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): Solar batteries are designed to withstand repeated charging and discharging cycles, with DoD indicating the percentage of the total capacity that can be utilized without significantly impacting battery lifespan.
- Cycle Life and Warranty: Battery lifespan is influenced by factors such as depth of discharge, temperature, charging/discharging rates, and maintenance practices. Manufacturers typically provide warranties specifying the expected cycle life and performance degradation over time.
- Compatibility with Inverter: Solar batteries need to be compatible with the solar inverter and charge controller to ensure seamless integration and efficient operation within the solar power system.
- Safety Features: Solar batteries incorporate safety features such as thermal management systems, overcharge/overdischarge protection, and battery management systems (BMS) to prevent damage, overheating, and safety hazards.
- Scalability and Expandability: Solar battery systems should be scalable and expandable to accommodate changing energy storage requirements and allow for the addition of multiple battery units or storage capacity as needed.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Advanced solar battery systems offer remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing users to monitor battery status, charging/discharging activity, and performance parameters via smartphone apps or online platforms.
- Grid Services and Backup Power: Solar batteries can provide various grid services such as peak shaving, load shifting, frequency regulation, and backup power during grid outages, enhancing energy reliability, and resilience.
- Environmental Impact: Lithium-ion batteries are preferred for solar energy storage due to their higher energy density, longer cycle life, and lower environmental impact compared to lead-acid batteries, which require proper recycling and disposal to minimize environmental contamination.
